A Comprehensive Guide To Otoscopes

- 1. A Comprehensive Guide To Otoscopes
- 1.1. Why an Otoscope is Essential?
- 1.2. Components of an Otoscope
- 1.3. Types of Otoscopes
- 1.3.1. Traditional Otoscopes
- 1.3.2. Video Otoscopes
- 1.3.3. Pocket Otoscopes
- 1.3.4. Pneumatic Otoscopes
- 1.4. Applications of Otoscopes
- 1.4.1. Diagnosis of Ear Infections
- 1.4.2. Earwax Removal
- 1.4.3. Monitoring Ear Health
- 1.4.4. Hearing Loss Assessment
- 1.5. Key Considerations When Purchasing an Otoscope
- 1.5.1. Optics and Light Source
- 1.5.2. Magnification
- 1.5.3. Durability and Build Quality
- 1.5.4. Ease of Use
- 1.5.5. Compatibility and Accessories
- 1.5.6. Power Source
- 1.6. Tips for Effective Otoscopy
An otoscope serves as a valuable instrument employed by both medical practitioners and individuals to inspect the ear canal and eardrum. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a parent keeping tabs on your child's ear health, or someone seeking a dependable otoscope for personal use, choosing the appropriate device is crucial. This all-encompassing guide will explore key factors to consider when acquiring an otoscope, showcase noteworthy device choices, and offer valuable insights to aid you in making an informed decision.
Why an Otoscope is Essential?
The human ear is a sophisticated and intricate structure, and the use of an otoscope enables a detailed inspection of the ear canal and eardrum. Healthcare practitioners depend on otoscopes to identify a range of ear-related conditions, including infections, blockages, and abnormalities. Likewise, possessing an otoscope at home can assist in keeping track of ear health, detecting potential issues in their early stages, and promptly seeking medical attention if necessary.
Components of an Otoscope
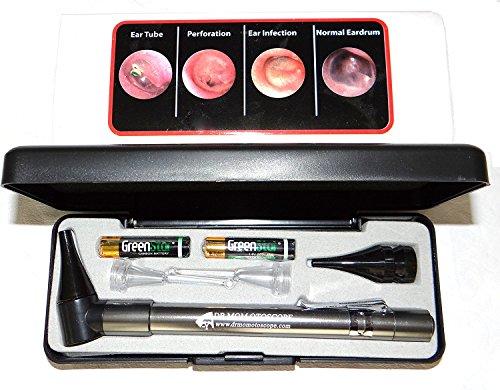
- Light Source: The primary function of an otoscope is to illuminate the ear canal, enabling healthcare professionals to visualize the structures within. Most modern otoscopes use LED lights, offering bright and consistent illumination.
- Speculum: The speculum is the cone-shaped attachment at the tip of the otoscope that is inserted into the ear. It helps in focusing the light and provides a clear view of the ear canal.
- Magnifying Lens: Some otoscopes come equipped with a magnifying lens, enhancing the visibility of ear structures. This is particularly useful for detailed examinations.
- Handle: The handle of an otoscope typically houses the power source, such as batteries. It may also include controls for adjusting the intensity of the light.
Types of Otoscopes
Traditional Otoscopes
These are the classic, handheld otoscopes with a direct viewing system. The practitioner looks through an eyepiece to observe the ear canal directly.
Video Otoscopes
Modern technology has given rise to video otoscopes, which incorporate a camera to capture images or videos of the ear canal. This allows for documentation and sharing of findings.
Pocket Otoscopes
Compact and portable, pocket otoscopes are suitable for practitioners on the go. They often lack some features of larger otoscopes but provide essential functionality.
Pneumatic Otoscopes
Incorporating a bulb for insufflation, pneumatic otoscopes are used to assess the mobility of the eardrum. This is particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions like otitis media.
Applications of Otoscopes
Diagnosis of Ear Infections
One of the primary uses of otoscopes is in the diagnosis of ear infections. By examining the ear canal and eardrum, healthcare professionals can identify signs of inflammation, fluid accumulation, or other indicators of infection.
Earwax Removal
Built-up earwax can cause discomfort and hearing issues. Otoscopes aid in visualizing the ear canal, allowing for the safe removal of excess earwax.
Monitoring Ear Health
Regular otoscopic examinations are crucial for monitoring ear health, especially in individuals prone to ear-related issues or those with chronic conditions.
Hearing Loss Assessment
In cases of unexplained hearing loss, otoscopic examinations are essential in ruling out structural issues within the ear.
Key Considerations When Purchasing an Otoscope
Whether you're a healthcare professional or an individual looking for a reliable device for at-home use, there are several key considerations to keep in mind when purchasing an otoscope.
Optics and Light Source
The quality of optics and the brightness of the light source are fundamental factors in ensuring clear visualization during ear examinations. Opt for otoscopes that feature high-quality optics to provide a sharp and detailed view of the ear canal and eardrum. LED illumination is highly recommended for its optimal brightness and color accuracy, allowing for a more accurate examination.
Magnification
The ability to magnify the ear canal and eardrum is essential for detecting subtle abnormalities that might be missed with the naked eye. Choose an otoscope with adjustable magnification levels to cater to different examination needs. This feature enhances the precision of the examination, making it easier to identify and assess ear conditions.
Durability and Build Quality
Durability is a key consideration for any medical instrument, and otoscopes are no exception. Look for devices constructed from high-quality materials such as stainless steel or robust plastics. These materials not only contribute to the longevity of the otoscope but also ensure it can withstand frequent handling and potential accidental drops.
Ease of Use
User-friendly features can significantly impact the overall usability of an otoscope. Consider devices with ergonomic designs, a comfortable grip, and intuitive controls to enhance ease of use. Additionally, opt for otoscopes that are easy to clean and maintain, as proper hygiene is essential in medical settings.
Compatibility and Accessories
Ensure that the otoscope is compatible with both disposable and reusable specula, which are the cone-shaped attachments used for ear examinations. This versatility allows for flexibility in choosing the right speculum for each examination. Check if the otoscope comes with additional accessories, such as ear specula in different sizes, to accommodate various patient needs.
Power Source
Otoscopes are available in both battery-powered and rechargeable options. The choice between the two depends on personal preference and convenience. Battery-powered otoscopes are often more straightforward and can be easily replaced when needed. Rechargeable otoscopes, on the other hand, provide a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option. Consider devices with long battery life or quick charging capabilities to ensure continuous and reliable use.
Tips for Effective Otoscopy
- Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting to illuminate the ear canal. LED lights are preferred for their brightness and longevity.
- Correct Speculum Size: Selecting the appropriate speculum size is crucial for a comfortable and accurate examination. A speculum that is too small may not provide a clear view, while one that is too large can cause discomfort.
- Patient Comfort: Explain the procedure to the patient beforehand to alleviate any anxiety. A calm and cooperative patient makes the examination smoother.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean and maintain otoscope components regularly to ensure optimal functionality and hygiene.
In summary, otoscopes have undergone significant advancements since their modest origins, transforming into advanced diagnostic instruments. Whether employed for regular examinations, identifying infections, or evaluating hearing impairments, otoscopes continue to play a vital role in healthcare. With ongoing technological progress, we anticipate continuous improvements in otoscope design, enhancing the precision and accessibility of ear examinations.